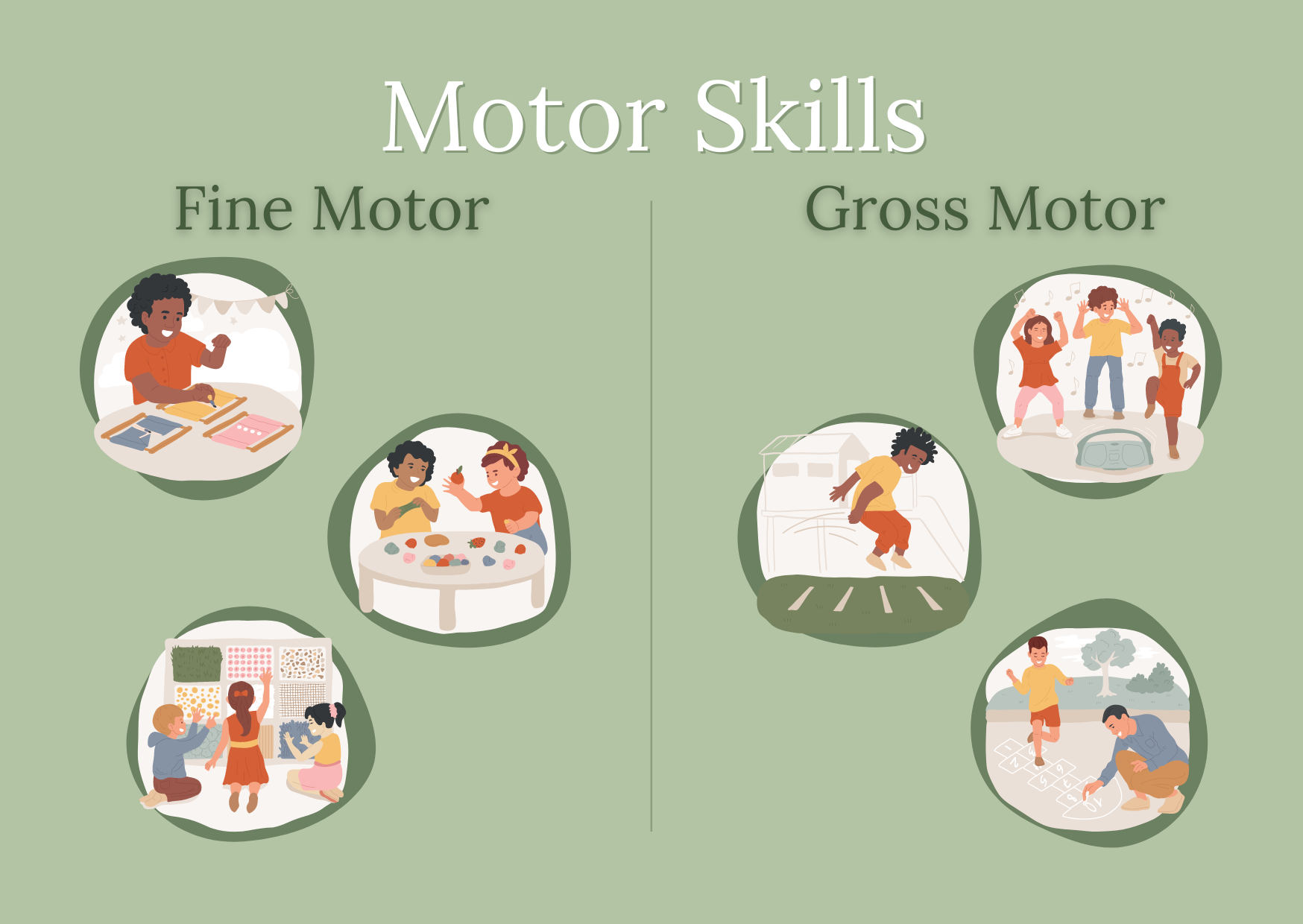
One of the primary focuses of pediatric occupational therapy is the enhancement of fine and gross motor skills. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, such as those in the hands and fingers, which are essential for tasks like writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. Gross motor skills, on the other hand, involve larger muscle groups used for activities like walking, jumping, and climbing. Pediatric occupational therapists use a variety of techniques and exercises to strengthen these skills, helping children gain the physical abilities they need for everyday activities.
To enhance fine motor skills, therapists often utilize activities that require precise hand movements and coordination. These activities might include:
- Pincer grasp exercises: Picking up small objects like beads or buttons.
- Handwriting practice: Using specialized tools to improve grip and stroke.
- Craft activities: Engaging in tasks like cutting with scissors or threading beads.
For gross motor skills, the focus is on larger movements and muscle groups. Techniques might include:
- Balance and coordination exercises: Using balance beams or obstacle courses.
- Strength-building activities: Climbing, jumping, and other physical play.
- Sports and recreational activities: Encouraging participation in age-appropriate sports to build muscle strength and coordination.
Many children experience sensory processing issues, where they struggle to accurately perceive and respond to sensory information. This can affect their ability to function in everyday environments, leading to challenges in school, at home, and in social settings. Pediatric occupational therapists are trained to identify sensory processing disorders and implement strategies to help children manage and respond to sensory stimuli more effectively.
Sensory integration therapy is a common approach used by occupational therapists. It involves play-based activities designed to help children process and respond to sensory information in a more adaptive way. Examples of sensory integration activities include:
- Swinging: Using swings to provide vestibular input.
- Deep pressure activities: Applying weighted blankets or pressure vests.
- Tactile play: Engaging with different textures through activities like finger painting or playing with sand.
Occupational therapists also work with parents and educators to create sensory-friendly environments. This might involve:
- Adjusting lighting: Using soft, natural lighting to reduce sensory overload.
- Reducing noise: Implementing soundproofing or using white noise machines.
- Organizing spaces: Creating designated areas for quiet time and sensory breaks.

In addition to physical and sensory needs, pediatric occupational therapy also supports cognitive and social development. Therapists work with children to improve attention, memory, problem-solving skills, and social interactions. These skills are critical for academic success and building positive relationships with peers and adults.
To support cognitive development, therapists might use:
- Memory games: Activities that challenge and improve memory skills.
- Problem-solving tasks: Puzzles and games that require critical thinking.
- Attention-building exercises: Activities that encourage sustained focus, such as reading or structured play.
For social development, occupational therapists might focus on:
- Social skills training: Role-playing and modeling appropriate social behaviors.
- Group activities: Encouraging participation in group play and cooperative tasks.
- Communication exercises: Helping children develop effective verbal and non-verbal communication skills.

Pediatric occupational therapy is an invaluable resource for fostering the overall development of children. By enhancing motor skills, addressing sensory processing issues, and supporting cognitive and social development, pediatric OT helps children achieve their full potential. Parents and caregivers who recognize the benefits of this specialized therapy can provide their children with the tools and support they need for a brighter, more independent future.
Pediatric occupational therapists are dedicated to helping children overcome challenges and reach their developmental milestones. Through personalized therapy plans and a holistic approach, they provide essential support that can make a significant difference in a child's life. Understanding the role of pediatric OT can empower parents to seek the right interventions and create a supportive environment for their child's growth and development.
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/occupational-therapy.html
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/25094-pediatric-occupational-therapy
.png)